Artificial Insemination
Artificial insemination is an assisted reproduction technique to achieve pregnancy, that is both simple and painless, and is fully performed on an outpatient basis. Your everyday life will remain exactly the same during treatment and medical examinations
What is artificial insemination?
Artificial insemination is an assisted reproduction technique whereby sperm is inserted in the woman’s uterus. Intrauterine insemination is a procedure widely used for treating several reproductive disorders. It should not be mistaken with In Vitro Fertilisation (IVF) as insemination aims to let fertilisation take place naturally within the fallopian tubes. The patient does not have to rest or interrupt her daily routine afterwards.
Types and indications for artificial insemination:
Donor sperm insemination for women without a partner
Artificial insemination is indicated for women who wish to pursue single motherhood and are in good general health, have an appropriate reproductive age, and possess a sufficient ovarian reserve. Otherwise, the success rates of this technique would be lower, and medical guidelines would recommend In Vitro Fertilization with donor sperm to optimize the chances of achieving pregnancy. During the first medical consultation, you will be guided on the most suitable technique for your particular case.
Artificial insemination with donor sperm for lesbian women
Artificial insemination in female couples is indicated when the patient who will carry the pregnancy presents adequate reproductive conditions, such as an age and ovarian reserve compatible with achieving pregnancy. Otherwise, the technique of artificial insemination with donor sperm will not provide favorable results, and In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) or the ROPA method will be the most suitable techniques.
Donor sperm insemination for heterosexual couples
- In cases of severe alterations in seminal quality.
- In failures of previous treatments involving other assisted reproduction techniques (in vitro fertilization with intracytoplasmic sperm injection or ICSI) due to a very severe male factor.
- In male genetic diseases where other treatments, such as prior preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD), have failed or are not accepted by the patients for personal reasons.
- Sexually transmitted diseases with repeatedly positive semen washes for infectious diseases such as Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C, Syphilis, or AIDS.
Husband/Partner sperm insemination
The ideal situation is for women up to 38 years old with a normal or acceptable ovarian reserve, permeable tubes, normal semen quality or with mild-to-moderate alterations, and a pregnancy search time of less than 3 years.
What examinations need to be performed before artificial insemination is advised?
We begin by collecting and studying our patients’ personal and family Medical History data.
In the case of female patients we perform:
- A complete gynaecological examination.
- Tests to estimate her Ovarian Reserve: A vaginal ultrasound to count the number of follicles produced during the first few days of the ovarian cycle (day 2 or 3 from the beginning of the menstrual period).
- Average counts of 6 to 12 follicles are regarded as normal at the beginning of the cycle.
- The number of follicles declines as women physiologically age.
- Measurements of hormones related to ovarian function (AMH, FSH, LH, E2) and other hormones (e.g. thyroid hormones).
- Tests to measure permeability of the fallopian tubes (not applicable to every case): Hysterosalpingography (HSG) or Hysterosonography (vaginal ultrasound whereby physiological serum is inserted into the uterus).
- Other: weight, height and blood pressure measurements.
In the case of male patients:
- A complete spermiogram
How is artificial insemination performed?
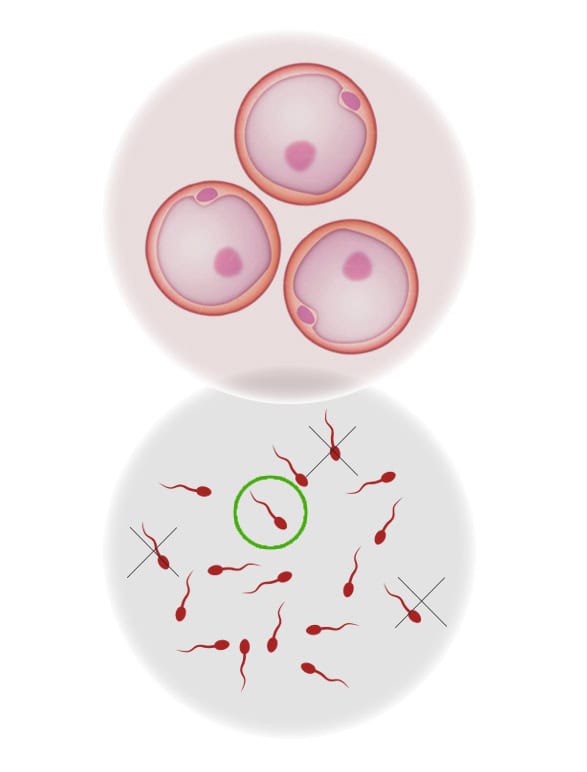
1. OOCYTE PREPARATION
It usually begins on the third day of the cycle with controlled ovarian stimulation through the administration of hormones that stimulate the growth of ovarian follicles, always following a personalized protocol for each case. This stimulation is monitored with 3 ultrasounds over approximately 8-10 days until an adequate ovarian response is obtained.
Subsequently, ovulation is triggered by an hCG hormone injection once an 18-20 mm follicle is confirmed via ultrasound. The day and time of the insemination are scheduled, generally 36 hours after the administration of hCG.
2. SPERM PREPARATION
Prior to the insemination, the seminal sample is prepared:
- HUSBAND/PARTNER’S SEMEN SAMPLE: Previously, about 2-3 hours before, the spouse will have provided a semen sample that will be capacitated in the laboratory to optimize seminal quality.
- DONOR SEMEN SAMPLE: In cases of insemination with donated semen, the selected sample is thawed for each woman according to blood group, Rh, and physical characteristics (phenotype).
It is important to clarify that donation in Spain is anonymous, meaning the patient cannot choose the donor.
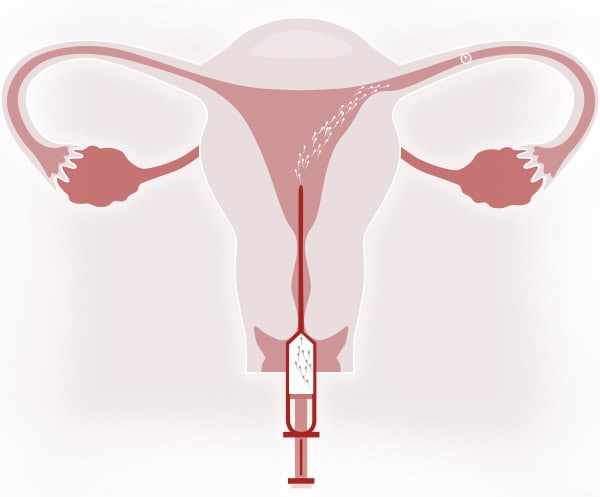
3.- INSEMINATION
It is a simple technique performed in the outpatient clinic. It does not require anesthesia, analgesia, or prior intake of anxiolytics and is not painful.
It is virtually similar to a routine gynecological examination:
- Placement of the speculum to visualize the cervix.
- Cleaning of the cervical mucus.
- Introduction of the cannula loaded with capacitated sperm through the external cervical os (ECO).
- Insemination of the sperm.
- Subsequently, the patient remains lying down for 10-15 minutes.
4. PREGNANCY CHECK
To determine the success of the treatment, a pregnancy test is performed in urine or blood after 15 days if menstruation has not occurred.
What are the positive pregnancy rates? What are the chances?
Statistically, the positive pregnancy rates after insemination with the partner’s sperm are 15%. Rates for insemination with donor sperm is slightly higher: 20-25%. This means a patient could accumulate a 45% of probability in 3 consecutive cycles in case of inseminations with the partner’s sperm and even higher in case of inseminations with donor sperm. At this point, it must be underlined that it is essential to perform an adequate examination and diagnosis so as to select those patients who best qualify for maximum probability.
| CUMULATIVE POSITIVE PREGNANCY TEST 3 cycles in the case of inseminations with husband’s or partner’s sperm | 45% |