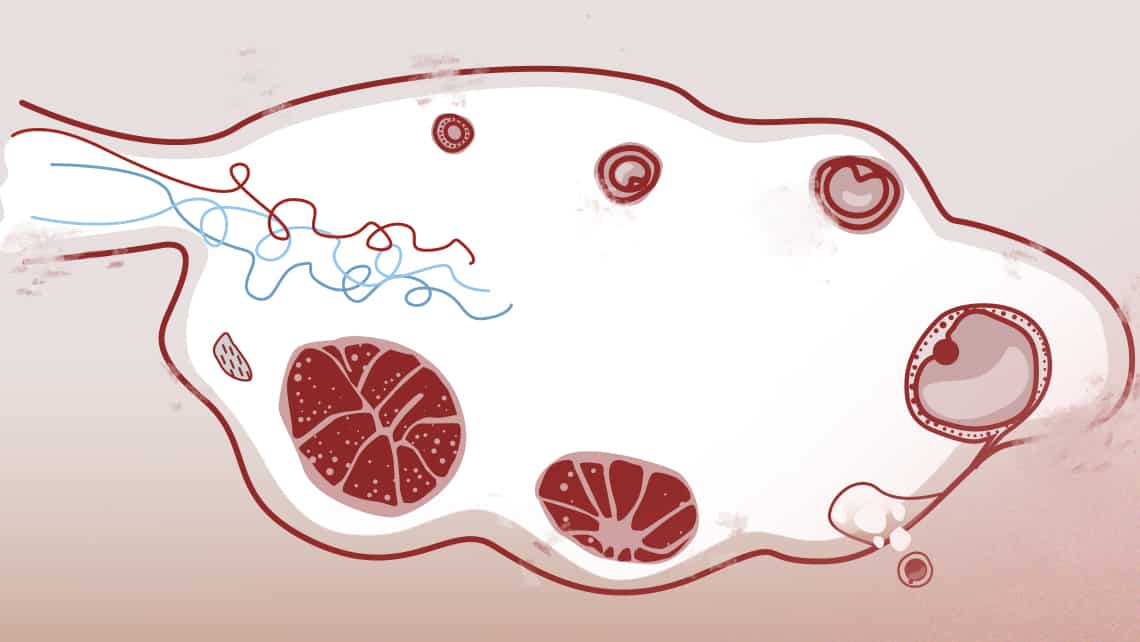
What are ovarian follicles? Number, growth and other characteristics
Índice
- 1 What are ovarian follicles?
- 2 Parts of the antral follicle
- 3 Why is important to know what is the endowment of follicles in each woman and their evolution throughout the ovarian cycle? How can we study it?
- 4 How many follicles should be in the ovary and what size should they be?
- 5 What is the dominant ovarian follicle?
- 6 How big do follicles have to be for egg retrieval (puncture)?
- 7 What is empty follicle syndrome (EFS)?
- 8 Can I find out the number of follicles and therefore my ovarian reserve during a routine check-up with my gynaecologist?
What are ovarian follicles?
To start with, let’s state what follicles are not. Follicles are not oocytes (eggs). Many patients confuse these terms, believing that follicle equals oocyte.
The female gamete is the egg, and the male gamete is the sperm. These are the cells involved in embryos obtained after fertilization.
Oocyte (ovum)

Sperm
Fertilized egg (embryo)
The follicle is a functional anatomical structure which forms part of the ovary and the egg is the cell that will mature in a microscopic part of inner wall of a follicle over spontaneous or stimulated ovarian cycle in normal conditions. Furthermore, the follicle contains other cell types which produce oestrogen required for normal development of the egg maturation.
The endowment of eggs is determined in the first weeks of life of the female embryo. From menarche (first menstruation) they will select, in each cycle an egg. Higher quality eggs are the first to be selected as with the passage of time, the eggs of the successive cycles have inferior quality. This explains why older women have more difficulty getting pregnant and have higher miscarriages rate.
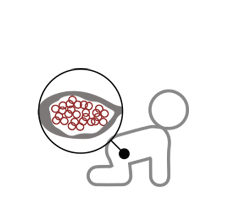



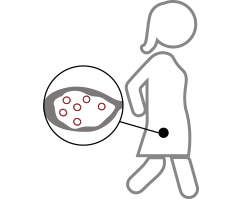
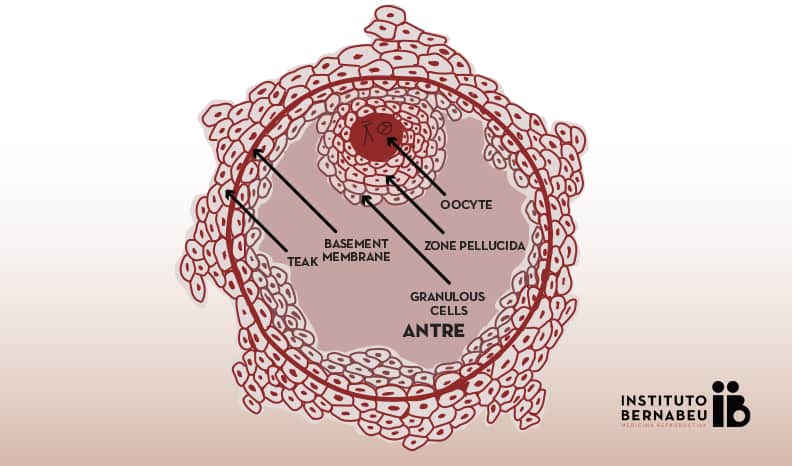
Parts of the antral follicle
The mature follicle is composed of:
- The oocyte, which has an external layer called the “zona pellucida”.
- A fluid filled cavity that is really what we see in the ultrasound.
- And a series of concentric layers that surround it:
- granulosa cells,
- and other cells that are called theca interna and externa cells. The basement membrane is located between these.
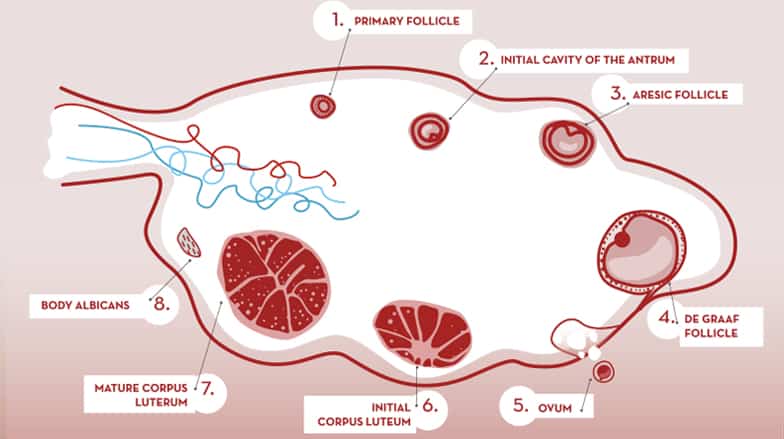
Ovarian cycle: follicular mellowing (follicular phase). Ovulation. Corpus luteum formation (luteal phase).
Why is important to know what is the endowment of follicles in each woman and their evolution throughout the ovarian cycle? How can we study it?
Within the study of female fertility it is essential to know what your ovarian reserve is. Hormonal analysis for assessment (hormone AMH, FSH, LH, estradiol, etc) and vaginal ultrasound in various forms are made.
Currently is still counting ovarian follicles, the truest estimate of ovarian reserve in a given patient. This reserve is expressed in number of follicles per ovary observed in the first days of the cycle (2nd to 5th) by performing a vaginal ultrasound. These follicles are called “antral”. Ultrasound also allows us to follow the evolution and growth of follicles both in spontaneous cycle as in a stimulated cycle fertility treatment.
How many follicles should be in the ovary and what size should they be?
Depending on the number of antral follicles, a woman is considered to have adequate or normal ovarian reserve if the count is 6-10. Low ovarian reserve, if the count is less than 6 ovarian reserve and high ovarian reserve if is greater than 12. Follicular size in this cycle phase is 2 to 10 mm.
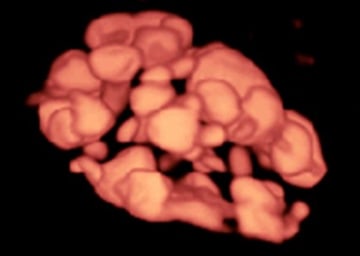
Image of ovarian follicles.Three-dimensional (3D) ultrasound in reverse mode 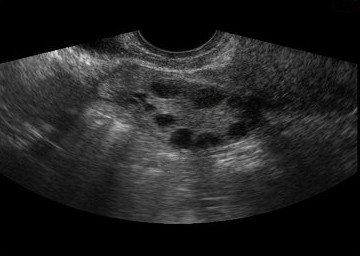
Image of ovarian follicles. Two-dimensional (2D) ultrasound
Women with low ovarian reserve are more likely to not respond to treatment and women with high ovarian reserve are responding in an exaggerated way. In both cases, it is more likely that the treatment cycle is cancelled than when the follicular count is normal.
What is the dominant ovarian follicle?
- In a natural cycle, from the antral follicles, one called “dominant” is selected. This follicle differs from the others by its size and rapid growth. Finally will be a mature follicle or De Graaf prepared to “ovulate”. The others atresian, that is they disappear or die as part of a programmed biological process. Before ovulation occurs, the average diameter of the dominant follicle is 22 to 24 mm (range 18-36 mm). It is the only marker that can predict ovulation with ease.
How big do follicles have to be for egg retrieval (puncture)?
- In stimulated cycle (hormonal treatment), generally, all or most of the antral follicles grow. The growth rate will be different for each of them. When several of them have reached a size of about 18 mm an hCG hormone (ovitrelle ®)that triggers ovulation is administered. The egg collection is scheduled 36 hours after administration of the hormone. The aim of treatment is to collect the most mature eggs that can then be fertilized by sperm.
However, the growth of a follicle does not always mean that contains within a mature egg.
As in a semen sample not all spermatozoa have enough quality to fertilize an egg and not all follicles contain mature eggs, or not all eggs have the same quality.
What is empty follicle syndrome (EFS)?
In a very small percentage of cases, it can be produce a called empty follicle syndrome. In this case, it would not be egg retrieval after ovarian stimulation in IVF treatment in patients with adequate growth follicles and estradiol levels (a hormone produced by cells lining the follicle wall). Its exact cause is unknown. Different situations have been considered as an error in the administration of hCG, abnormal response to treatment, impaired follicular mellowing. No clear predisposing factors that could help to estimate or establish their possible occurrence but has been observed more frequently in women with a history of primary infertility (women who have never been pregnant) and having good follicle count. It is a rare event (<7%), but its incidence increases with age. The patient that this does not imply this, in most cases, a fertility problem. In fact, most have a normal follicular mellowing and number of egg.
You can learn more about Empty Follicle Syndrome at the following link
Can I find out the number of follicles and therefore my ovarian reserve during a routine check-up with my gynaecologist?
To conclude, I would like to emphasize that any woman, even when not considering seeking pregnancy at present, can found out with a simple count of follicles during a routine gynaecological ultrasound check-up, their ovarian reserve. Thus, a considerable percentage of women could know in advance if this is appropriate or not. Perhaps, many people would try to get pregnant before if they knew this condition. Do not forget the ovary, unfortunately, is an organ that gets “tired” soon. It has half of the life compared with other organs.
Dra. Lydia Luque, Gynaecologist at Instituto Bernabeu.
IT MAY ALSO BE OF INTEREST TO YOU
- In vitro fertilization treatment
- Poor Ovarian Response Unit
- Double stimulation: is it possible to recover more oocytes in patients with low ovarian reserve?
- I’m not getting pregnant. Why not? What can I do about it?
- Pharmacogenetics for the treatment of low ovarian response
- Premature Ovarian Failure, Can I be a mother? Causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment and prevention
